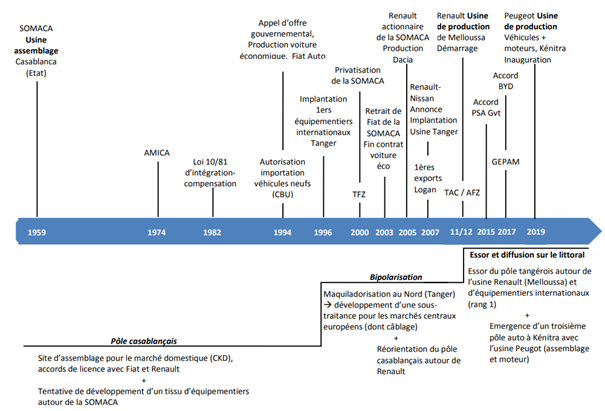
In the space of two decades, Morocco has risen to become the leading automotive hub on the African continent, combining production, exports, and innovation. This success is based on the state’s strategic vision, a competitive industrial environment, and cutting-edge infrastructure that have attracted major global manufacturers.
- Major industrial projects
Morocco relies on two major industrial pillars:
-
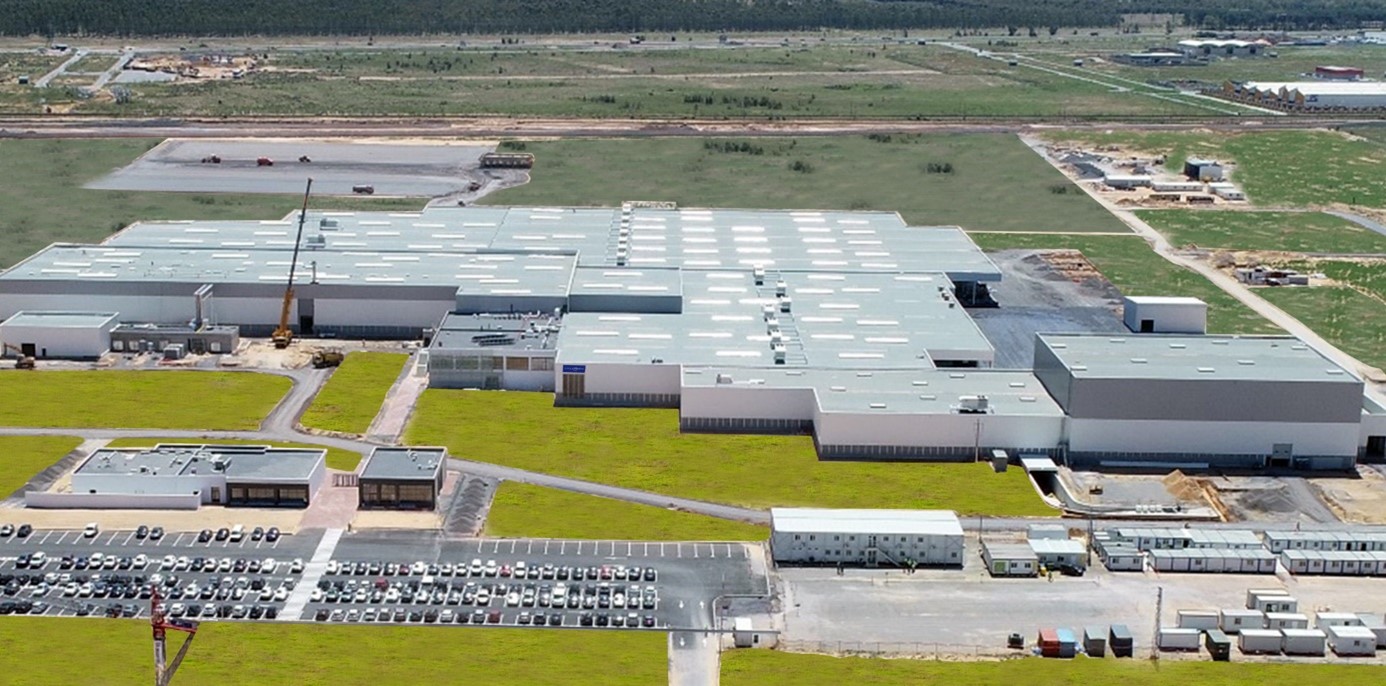
- Renault Tangier Med: Operational since 2012, the Renault-Nissan group plant in Tangier is the largest in Africa. With an annual capacity of more than 400,000 vehicles, it primarily assembles Dacia models (Logan, Sandero, Dokker) for Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. The plant is certified for its low carbon impact, thanks to the use of renewable energy and the recycling of industrial water.
- Stellantis Kenitra: inaugurated in 2019, the PSA group factory (now Stellantis) in Kenitra has a capacity of 200,000 vehicles per year, with the potential to expand to 300,000. It notably produces the Peugeot 208 and incorporates cutting-edge technologies: robotization, automated quality control, and flexible lines to quickly adapt to model developments.
Manufacturers are also relying on a dense network of local subcontractors, with more than 250 equipment manufacturers located in specialized industrial zones (Tangier Automotive City, Atlantic Free Zone, etc.), producing wiring, seats, electronic components, etc.
- Logistics infrastructure
The development of the Moroccan automotive sector has been made possible by massive investments in infrastructure:
-
- Port Tanger Med: Africa’s leading container port, it offers direct connections with more than 180 ports worldwide and logistics adapted to the mass export of vehicles.
- Motorway and rail network: modern axes connect factories to ports and major urban centers. The TGV (Al Boraq) also facilitates connections between Tangier, Kenitra and Casablanca.
- Towards electrification
Morocco isn’t limited to thermal vehicles. Manufacturers and the government have initiated projects to:
-
- develop assembly lines for electric and hybrid vehicles;
- produce batteries and key components locally, based on the national renewable energy strategy (particularly solar and wind).
- Ambitions 2030
Morocco aims to:
-
- A production capacity exceeding 1 million vehicles per year.
- Increased integration of local components to achieve a local content rate of over 80%.
- The creation of tens of thousands of additional direct and indirect jobs in the sector.
With its structuring projects, Morocco aims to become a key player in the transition towards a sustainable automotive sector in Africa and beyond.